Leading the Future, with Enerjisa Executive Team, Istanbul
November 20, 2024 at Enerjisa, Istanbul

Welcome to the future, right now.
Superfast-gaming chips and fat-busting superdrugs, asteroid-chasing rockets and carbon-capturing technologies, 4 day working weeks and chess reinvented as a reality TV game, health-enhancing fashions and the rebirth of the hairy mammoth. Nvidia is transforming tech, while Novo Nordisk innovates healthcare, KinetX changes the space race, while Climeworks eliminates carbon.
We used to marvel at innovations with a leap of imagination. Ideas and technologies that promised to transform our world, but seemed a little out of reach. Now, science fiction has collided with practical reality, powered by mind-boggling technologies that are evolving at incredible speed, but also rapid social and cultural change, accelerating human possibilities into practice.
Next is now, not only because of the pace of innovation, but also the convergence of pathways – technologies, industries, customers, applications and expectations.
What’s happening in gaming today, shapes new experiences in retail or finance. New possibilities of space travel accelerate the evolution of EVs. Clean energy meets green cement. Pharma tech meets fashion tech. Physical and digital are one, fast developing markets outpace the old stagnated developed markets, and GenZ outthink their GenX leaders.
The future is already here, even if it’s unevenly distributed. Curiosity drives creativity, enabled by new capabilities to address the biggest challenges. So what could you do? What’s your vision of next, and how do you start now?
- 24 for 2024 … new ideas, new innovators, new possibilities
- Future Recoded … an online learning and knowledge platform
- Trend Kaleidoscope 2024 … curating all the best trend reports
- Megatrends and Strategies … defining your future strategy roadmap
- Waveriders and Transformers … developing leaders as future makers
Colossal, the de-extinction company
Colossal Biosciences seeks to reawaken the past, to bring back extinct species, to expand endangered populations through genetic rescue, to support biodiversity. In a world pushed to the brink, Colossal is optimising conservation, exogenous development, bioinformatics, modern genetics, cellular engineering, paleogenetics, biodiversity, genomics, embryology, stem cell reprogramming, computational biology, artificial intelligence, bioethics, and de-extinction.
The Austin-based genetic engineering company, founded by geneticist George Church and entrepreneur Ben Lamb, is working to de-extinct the woolly mammoth, the Tasmanian tiger, and the dodo.
Because the woolly mammoth and Asian elephant share 99.6% of the same DNA, Colossal is seeking to develop a proxy species by swapping enough key mammoth genes into the Asian elephant genome. Key mammoth genealogical traits include: a 10cm layer of insulating fat, five different types of shaggy hair, and smaller ears to help the hybrid tolerate cold weather.
Colossal launched as a fully-fledged business in 2021, with a mission to preserve endangered animals through gene-editing technology and use those same animals to reshape the world’s natural ecosystems to combat climate change.
Colossal’s lab will pair CRISPR/Cas9 with other DNA-editing enzymes, such as integrases, recombinases, and deaminases, to splice woolly mammoth genes into the Asian elephant. The company plans on sequencing both elephant and mammoth samples in order to identify key genes in both species to promote population diversification. By doing so, Colossal hopes to prevent any rogue mutations within the hybrid herd.
Back in a 2008 interview with The New York Times, George Church first expressed his interest in engineering a hybrid Asian elephant-mammoth by sequencing the woolly mammoth genome. In 2012, Church was part of a team that pioneered the CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing tool, through which the potential for altering genetic code to engineer the envisioned “mammophant” surfaced. He presented a talk at the National Geographic Society in 2013, where he mapped out the idea of Colossal.
Church and his genetics team used CRISPR to copy mammoth genes into the genome of an Asian elephant in 2015. That same year, his lab integrated mammoth genes into the DNA of elephant skin cells; the lab zeroed in on 60 genes that experiments hypothesized as being important to the distinctive traits of mammoths, such as a high-domed skull, ability to hold oxygen at low temperatures, and fatty tissue. By 2017 it had successfully added 45 genes to the genome of an Asian elephant.
While Colossal’s de-extinction business might seem like science fiction, the latest movie from Jurassic Park, it echoes the progress by companies like CRISPR Therapeutics in Zurich, led by Nobel prize winner Jennifer Doudna, who applying the same science to humans. With all the same technical and ethical challenges which it brings. It also demonstrates how rapidly ideas of fiction are now becoming reality.

- Big Ideas Report 2024 … how tech is transforming business
- Future Possibilities Index 2024 … the next economies emerging right now
- Global 50 Opportunities 2024 … megatrends driving new opportunities
- 100 Reasons to Love the Future … new narratives that give hope amidst uncertainty.
Innovations enabled by incredible technologies
The new Big Ideas report by ARK Invest captures the disruptive impact of technologies right now. It suggests that by 2030, the convergence of 5 significant technologies, accelerated by artificial intelligence, will have an unprecedented economic impact. AI provides the “intelligent glue” to bring together the potential of public blockchains, multigenomic sequencing, energy storage, and robotics, in a way that could transform global economic activity more significantly than any previous industrial revolution.
Globally, real economic growth could accelerate from 3% on average during the past 125 years to more than 7% during the next 7 years as robots reinvigorate manufacturing, robotaxis transform transportation, and AI amplifies knowledge worker productivity.
As a result the global equity market value specifically associated with disruptive innovation could increase from 16% of the total to more than 60% by 2030, resulting in annualised equity returns of 40%, or increasing the total market capitalisation driven by disruptive tech from $19 trillion today to roughly $220 trillion by 2030.
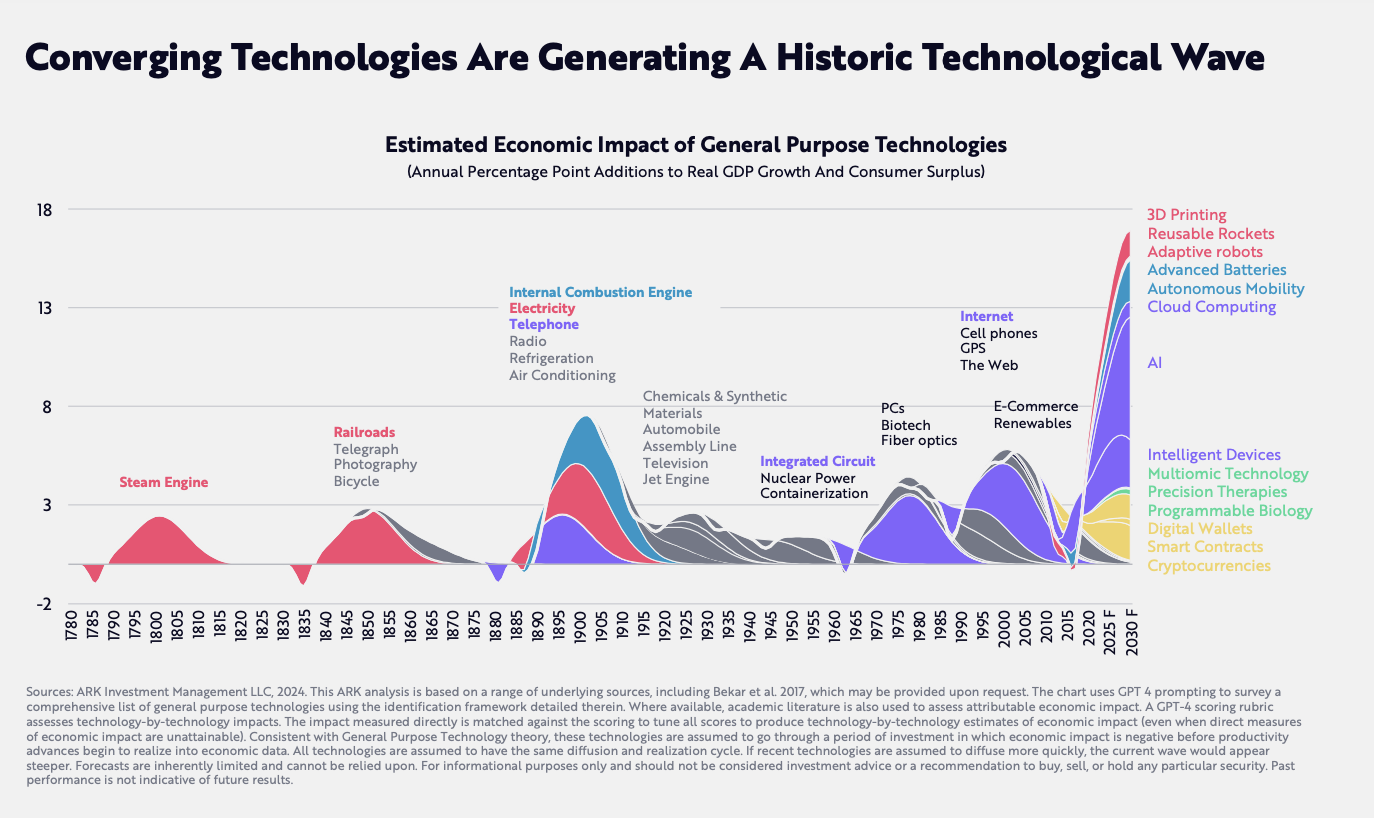
The Future Possibilities Index 2024 also explores the applications of these fast-emerging tech, and how they will shape new economies. It focus on 6 transformational trends that are creating possibilities and the factors that determine our readiness and capacity to leverage these trends over the next 5-10 years. All have emerged from a combination of new business models, technologies, and changes in attitudes and behaviours. The six trends are the Exabyte Economy, the Wellbeing Economy, the Net Zero Economy, the Circular Economy, the BioGrowth Economy and the Experience Economy.
Fast Company’s latest ranking of the world’s Most Innovative Companies 2024 showcases some of the most exciting innovators who are both driving this tech acceleration, and embracing its benefits. While BCG also produces an innovation ranking each year, quantitatively evaluating the R&D efforts of corporations, the FC version is far more insightful, about the people driving the innovations, and the solutions that are emerging.
This year’s #MIC24 ranking includes:
- Nvidia is riding a wave of warp-speed AI progress, having lagged far behind Intel for decades, Jensen Huang’s $1.5 trillion business which he founded in 1993 on his 30th birthday, leapt ahead of tech monoliths like Alphabet and Amazon in recent months, driven by the rush for high-powered immersive gaming, and the relentless growth of AI.
- Novo Nordisk found in its latest diabetes drug Ozempic, an obesity-busting sensation, that together with its lower dosage sister-brand Wegovy, has taken the world by storm. The Danish pharma business can’t make enough of it, and has soared to become Europe’s most valuable company, and more valuable than Denmark’s entire GDP.
- Perplexity is creating an entirely new way to search the web, by leveraging AI to provide more contextualised and accurate answers, rather than a list of relevant links. It uses a combination of homegrown large language models (LLMs) and third-party models (like OpenAI’s GPT-4) plus retrieval-augmented generation (RAG).
- KinetX helped navigate a spacecraft on a 4.4 billion-mile mission to land on an asteroid and return home. Founded in 1992 as a spinoff of Lockheed Martin, it is partnering NASA on deep-space missions like New Horizons (to Pluto, then the edge of the solar system) and Messenger (orbiting Mercury for the first time).
- Climeworks uses direct air capture to scrub carbon from the atmosphere. It operates the world’s largest DAC plants, both in Iceland, which remove around 10,000 tons of CO2 from the atmosphere every year—and about half of that is being done by the Zurich-based DAC pioneer.
Innovations enabling radically better lives
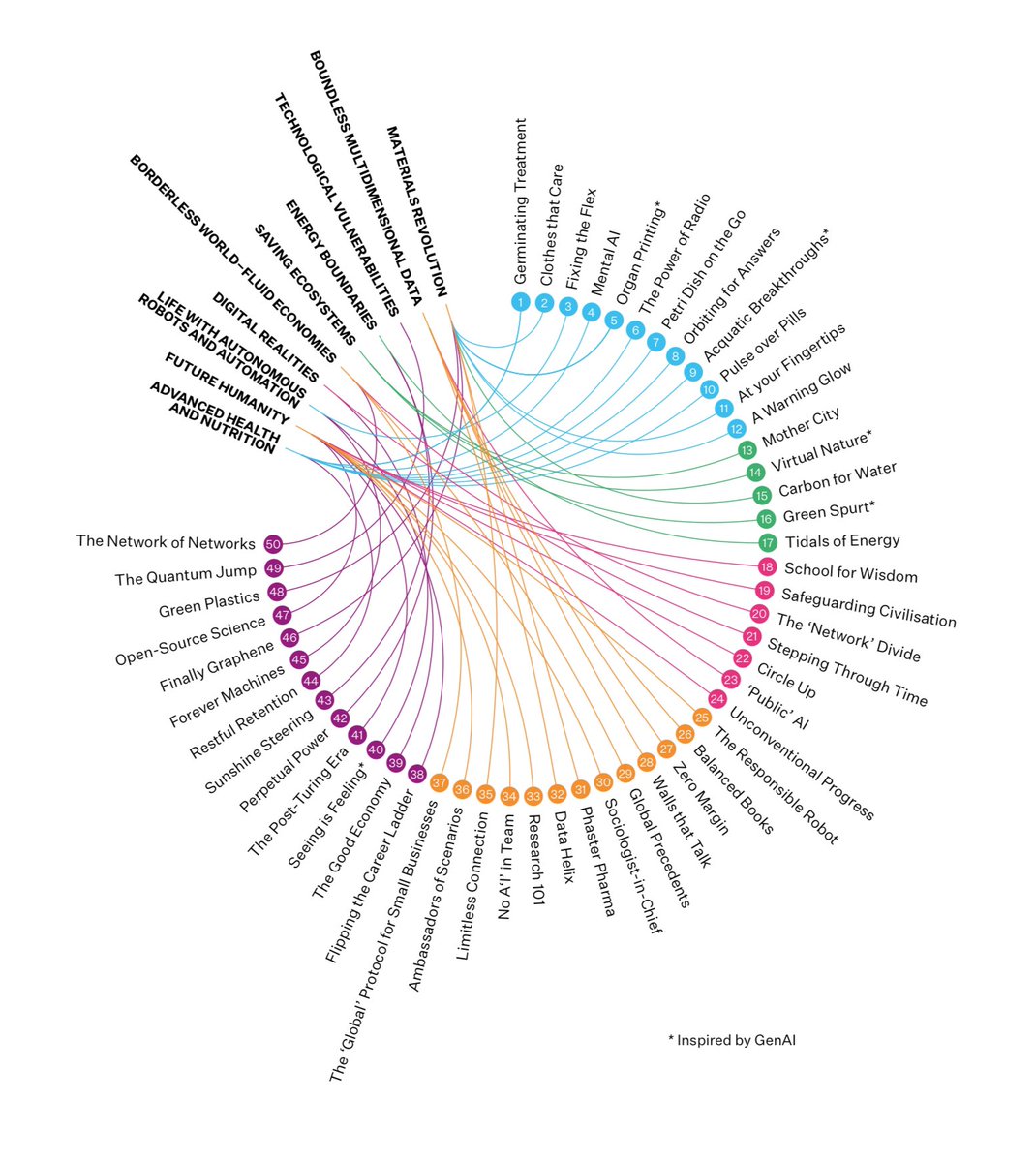
The new Global 50 Opportunities report by Dubai Future Foundation takes a global perspective on the innovative applications emerging from a rapidly changing world, partly driven by technologies, but much more too.
It starts by exploring the megatrends which it sees as most influential right now, and then how these are unlocking 50 opportunities for future growth, prosperity and well-being. Some opportunities may be in their early days of exploration, some require reflection, and some feel very far away. “Shaping the future cannot be done by just waiting for it but rather by utilizing the latest technologies and knowledge tools and meeting its challenges starting from today.”
The 8 megatrends include materials revolution (from which opportunities emerge like 3d printing of human organs, green plastics, and fashion with embedded health benefits), future humanity (school for wisdom, open source science, and flipping career ladders), and advanced health (mental AI, pulse over pills, and biohacking 2.0). These are just a few examples (dive into the digital report to explore the opportunities in more detail):
100 Reasons to Love the Future is a fabulous new report from AXA’s foresight team, promising “new narratives of hope” and inspiring us to “imagine utopia rather than retreat to dystopia”. The report argues that in a world of escalating risks, our societies and economies cannot afford to become paralysed by uncertainty. We are all living through a deep transformation. Far better to embrace it than retreat into anxiety and doubt.
In the midst of the 100 reasons is a great insight from Plurality University about what organisations could look like in 2050 – from the Marketrix to the Reactivator, the Enterpocine and the Zombinc. There’s also a great insight about Te Korekoreka, and navigating futures with Māori Wisdom. The New Zealand initiative uses social innovation to achieve equity in education, employment, and income for Māori people. And much more, a great report!
Take another look at Fast Company’s Most Innovative Companies 2024 list, and beyond the big names like Nvidia you will find a wealth of smaller companies making significant human impacts, harnessing tech for good, rather than just for tech. Yet the new tech capabilities are incredible, providing new ways to solve some of the biggest problems; while also shaping cultures through exponential social influence; and enabling people to access, and do, what they could never before:
- Solfácil the Brazilian solar investment company is bringing solar power to people living in the Amazon, and has financed approximately $450 million in solar loans, working with more than 4,250 active solar installers and has 66,000-plus customers to date.
- 4 Day Week Global convinced companies around the world to adopt a shorter work week, the nonprofit brought together hundreds of companies to create a post-pandemic revolution in the workplace, encouraged by its research which showed that a 4 day week delivered an average 36% rise in revenue.
- Chess.com is turning a centuries-old game into must-see reality TV. The freemium chess platform logged more games played (12.5 billion) than ever before, while establishing itself as the game’s cultural hub, full of everything from news to memes to the best Twitch streamers.
- Sea Forest, a Tasmanian business which scooped the 2023 Earthshot Prize, has a seaweed supplement to stop cows from burping up methane. It is the first company in the world to farm methane-busting Asparagopsis, a red seaweed native to Australian coastal waters, reducing methane production by up to 90%.
- Mattel took its 65 year old Barbie dolls and turned the brand into a $1.4 billion global movie blockbuster, the highest grossing film of 2023, with a series of agenda-setting messages not just saccharine sassiness, and became a cultural event that attracted diverse audiences, plus all types of pink-coloured spinoffs.
So while the world of technology is complex and relentless, with profound questions about ethics and humanity, our rapidly changing world can also be deeply human, sometimes frivolous, sometimes profound.
The opportunities to innovate are everywhere. And while average, old markets might seem to have stagnated, the world continues to move forwards at incredible pace. We have huge challenges, where issues like climate change will only be conquered with radical new thinking, and enabled by new technologies.
We also have an opportunity to create a happier, healthier world. Embrace utopia, don’t retreat to dystopia. By jumping to the future we can see problems differently, the impossible becomes possible, and we can accelerate progress.
Next is now. There is only ever today. Let the future begin.
What’s the future of energy?
The energy transition dominates many business agendas, both in the energy sector as companies seek to shape the future markets, and in other industries as they seek to reduce emissions.
While some will focus on the relative merits of wind, solar and hydro – adding in geothermal, biomass and hydrogen – others will focus on the challenges of migration, adoption and regulation – and more generally on optimising energy generation, storage and distribution.
Battery technology enables us to store excess energy generated by renewable sources such as solar and wind power, making them more reliable and flexible. Smart grids, which use sophisticated algorithms to balance supply and demand, are another key trend that is helping to optimize the use of renewable energy.
Recognising the limitations of land, and the use of previously farming or domestic land for energy generation, the sea is the next frontier (and then space of course, with asteroid mining and more!). Orsted is leading the development of wind islands, elsewhere floating solar platforms, tidal energy, and bioenergy from algae.
- Solar, South Korea … The world’s largest floating solar power platform is currently being developed in South Korea. It’s located near Saemangeum, an estuarine tidal flat on the coast of the Yellow Sea. This impressive 2.1 GW floating solar farm is part of a planned mega renewable energy project that aims to generate up to 3 GW of electricity in the Yellow Sea. Once operational, it’s expected to provide enough electricity to serve the needs of approximately one million homes
- Geothermal, Iceland … 85% of Iceland’s energy needs are met through geothermal energy, making it one of the world’s leaders in this field. The Hellisheidi Geothermal Power Plant is the world’s largest geothermal power plant and generates 303 MW of electricity. Geothermal energy is a renewable energy source that uses the natural heat of the Earth to generate electricity without emitting greenhouse gases.
- Tidal, Scotland … harnessing the power of ocean tides to generate electricity, the MeyGen project in Scotland is a notable example of this technology in action. The project involves the installation of tidal turbines in the Pentland Firth, which is known for having some of the strongest tides in the world. The project has the potential to generate up to 398 megawatts of electricity, which is enough to power approximately 175,000 homes.
- Hydrogen, Japan … Fuel cell vehicles powered by hydrogen fuel cells are already on the market, with companies like Toyota and Honda leading the charge in this area. In Germany, a hydrogen fuel cell-powered train called the Coradia iLint has been developed as an alternative to diesel trains. The train emits only water vapor and has a range of up to 600 miles on a single tank of hydrogen.
- Bioenergy, UK … Drax power station is exploring the use of bioenergy with carbon capture and storage (BECCS) to capture and store carbon dioxide emissions from biomass combustion. This technology has the potential to achieve negative emissions, effectively removing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
However generating the energy is only the starting point.
Smart grid systems are being implemented in many countries to optimize the distribution of renewable energy and reduce energy waste. For example, in the United States, Pacific Gas and Electric Company has implemented a smart grid system that allows customers to monitor their energy usage in real-time and receive alerts during peak energy usage periods.
AI-enabled energy management systems are being developed to optimize energy usage and reduce energy waste. For example, Siemens has developed a system called the EnergyIP Smart Grid Platform that uses AI to analyze data and provide real-time energy management solutions.
- Most Innovative Companies in Energy 2023 by Fast Company
- Twelve: The Carbon Transformation Company
- LanzaTech: turning emissions into fuel by CNN
- Watty: energising the smart home
- Top 10 Renewable Energy Companies by Energy Acuity
- Examples of 3 energy companies using new business models by EnergyPost
- Remodelling the future: energy transition driving new models by CapGemini
- 7 future utility business models by PwC
- Utilities new business models, by IDC/CapGemini
- Energy as a service by Recanteur
Objectives
- Explore the drivers of future change, learning from the world’s most innovative companies
- Consider the challenges and opportunities of disruption, and specifically related to data
- Evaluate alternative future scenarios, and how we help our clients develop better futures
- Explore what innovation and transformation, means for every part of our business
- Reflect on what it takes to lead today and tomorrow, to be a performer and transformer.
Agenda
Session 1: World Changing
- Riding the waves of change – purpose, profits and value creation
- Customer agendas, health to home, social to sustainable
- Rethinking everything, discontinuities and disruptors
- Inspired by SpaceX and Biontech, Jio and DBS
Session 2: Future Scenarios
- Exploring alternative futures, change drivers and uncertainties
- Strategies and plans, making choices from the future back
- Building a future portfolio, to exploit and explore
- Inspired by the rapidly changing world of mobility
Session 3: Moonshot Innovation
- Moonshots and Gamechangers, breaking free of old mindsets
- Human and tech, customer and brands, sustainable and better
- Rethinking the future of energy, beyond traditional boundaries
- Inspired by Google and Twelve, Northvolt and Lanzatech
Session 4: Business Models
- 10 types of innovation, new business models and ecosystems
- Business models as a source of competitive advantage
- Dynamic business modelling and transformation
- Inspired by Seimens and Tesla, Schneider and Orsted
Session 5: Winning Leaders
- What it takes to be a “Performer Transformer” – in mindset, roles and actions
- Creating tomorrow while delivering today, turning purpose into practical action
- Using the catalyst of external change to drive and guide your internal change
- Inspired by Satya Nadella, Anne Wojcicki, Melanie Perkins and Hamdi Ulukaya
The energy sector has been undergoing significant transformations, with emerging business models reflecting the changing landscape. Here are some new and evolving business models in the energy industry:
- Energy as a Service (EaaS): This model involves providing energy solutions as a service rather than a commodity. Companies offer comprehensive energy services, including generation, storage, and management, with customers paying for outcomes rather than infrastructure.
- Virtual Power Plants (VPPs): VPPs aggregate the capacities of multiple distributed energy resources (DERs) like solar panels, wind turbines, and energy storage systems. By centrally managing these resources, VPPs can provide grid services, optimize energy use, and enhance reliability.
- Blockchain-Based Energy Trading: Blockchain technology enables transparent and secure peer-to-peer energy transactions. Consumers with renewable energy sources can sell excess energy directly to others on a decentralized platform, bypassing traditional energy providers.
- Demand Response Platforms: These platforms enable consumers to adjust their energy consumption based on real-time pricing or grid demand. Businesses and individuals can receive incentives for reducing energy usage during peak periods or when the grid is under stress.
- Community Solar: Community solar projects allow individuals or businesses to invest in or subscribe to a shared solar facility. Participants receive credits on their electricity bills based on the energy generated by the communal solar installation.
- Energy Storage as a Service (ESaaS): This model involves offering energy storage solutions on a subscription or pay-as-you-go basis. Customers can benefit from energy storage without the upfront costs and complexities of ownership.
- Microgrids and Nanogrids: Microgrids are localized energy systems that can operate independently or in conjunction with the main grid. Nanogrids are even smaller, serving a single building or a small community. These systems enhance resilience, provide energy security, and support the integration of renewables.
- Peer-to-Peer Energy Trading Platforms: Platforms enable individuals or businesses with renewable energy sources to directly sell excess energy to nearby consumers. Blockchain technology or other secure systems facilitate transparent and automated transactions.
- Energy Efficiency as a Service (EEaaS): Companies provide energy efficiency solutions to businesses on a subscription or performance-based model. Customers pay based on the energy savings achieved through implemented efficiency measures.
- Circular Economy Models: Companies are exploring circular economy principles, where energy systems are designed for longevity, reuse, and recycling. This involves a shift from a linear “take, make, dispose” model to a more sustainable and circular approach.
Here are some of the players at the forefront of shaping the future of energy:
- Tesla: While often associated with electric vehicles, Tesla is also a major player in energy innovation. The company is involved in the development of energy storage solutions (Powerwall, Powerpack, and Megapack), solar products, and grid management systems.
- Enel: An Italian multinational energy company, Enel has been actively pursuing a transition to renewable energy. The company is involved in wind, solar, and hydroelectric power projects and is known for its commitment to sustainability and innovation.
- Orsted: Formerly known as DONG Energy, Orsted is a Danish energy company that has undergone a transformation, shifting its focus from fossil fuels to renewable energy. It is a global leader in offshore wind power.
- NextEra Energy: Based in the United States, NextEra Energy is one of the largest renewable energy companies globally. It has a significant presence in wind and solar power generation and is known for its forward-looking approach to clean energy.
- Vestas Wind Systems: A Danish company, Vestas is a leading player in the wind turbine manufacturing industry. It is known for its innovations in wind turbine technology and has a global presence in the wind energy market.
- Pattern Energy Group: Specializing in renewable energy, Pattern Energy is involved in the development, ownership, and operation of wind, solar, and transmission assets. The company focuses on sustainable and responsible energy solutions.
- Siemens Energy: Siemens Energy is a global player in energy technology, providing solutions for power generation and transmission. The company is involved in both conventional and renewable energy technologies and is actively working on innovations in the energy sector.
- BloombergNEF (BNEF): While not a traditional energy company, BloombergNEF is a research organization providing insights into clean energy, advanced transportation, and sustainable industries. It tracks and analyzes trends and innovations in the energy sector.
More from Peter Fisk
- Next Agenda of best ideas and priorities for business
- Business Futures Project collating all the best ideas
- Megatrends 2030 in a world accelerated by pandemic
- 49 Codes to help you develop a better business future
- 250 companies innovators shaking up the world
- 100 leaders with the courage to shape a better future
- Education that is innovative, issue-driven, action-driving
- Consulting that is collaborative, strategic and innovative
- Speaking that is inspiring, topical, engaging and actionable